Abstract
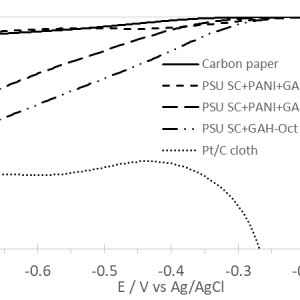
Heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots (CQD) were synthesized by 3 preparation methods: pyrolysis, microwave irradiation, hydrothermal synthesis. Their properties as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline conditions were studied by linear sweep voltammetry. The best properties for N-doped CQD were obtained for hydrothermally synthesized CQD with an onset potential of 0.85 V vs RHE. Co-doping with a second heteroatom, B or S, improved the electrocatalytic properties further with the best performance obtained for B-N co-doping with an onset potential of 0.87 V vs RHE. The influence of an anion exchange ionomer (AEI) on the properties was also studied using 5 AEI with different backbone hydrophilicity and side-chain length. The best properties were observed for a composite electrode combining B-N co-doped CQD and a poly(2,6-dimethylphenylene oxide) with quaternary ammonium groups grafted on pentyl side-chains with an onset potential of 0.94 V vs RHE, which is among the highest in the literature.
Illustrations
Details
Published on: European J.Materials 2023, 3, 2240350.
Authors: Knauth P.; Sgreccia E.; Nallayagari A.R.; Pasquini L.; Narducci R.; Di Vona M.L.